|
Table of Content Volume 3 Issue 2 - August 2017
Sexual diamorphism of frontal sinus in north Karnataka region
Vrushali P Karadkhelkar1, S V Kshirsagar2*
1Assistant Professor, 2Professor and HOD, Department of Anatomy, Bidar Institute of Medical Sciences, Bidar, Karnataka, INDIA. Email: sonysadu@gmail.com
Abstract In forensic science finger prints, foot prints, dental patterns, bones, skulls, sutures are the commonly used tools for identification of an individual. Recently paranasal sinuses have attracted attention of anatomist anthropologist, forensic experts. Availability of even a small piece of frontal bone containing an intact frontal air sinus is sufficient for purpose of identification as well as knowing sex. Present study is conducted on 80 individuals. Frontal sinus study is carried out by taking radiographs. These radiographs are minutely studied under the heading of height, breadth, surface area with the help of three different methods. ‘t’ test is applied and sex is determined with available resources. ‘t’ test shows significance for all parameters. Various workers have studied frontal sinus. In present study we have compared above measurements with the previous studies. It is observed after detail study that the conclusion of present study is similar as the previous studies. Key Words: Frontal sinus, sex determination, radiograph, ‘t’ test
INTRODUCTION There are two frontal sinuses posterior to the supercilliary arches, lie in between outer and inner table of frontal bone. In living to palpate the sinuses, it lies a triangular area 3 cm above the nasion and a junction between medial 1/3 and lateral 2/3 of supra-orbital margin. Two sinuses are rarely symmetrical. The septum between them usually deviates from the median plane. The average measurements:
Main function of sinus is to resonance to voice and to lighten the weight of skull. But saving in weight is trivial as absence of sinus does not add any weight to skull also there is no any change of volume of skull. Extensive studies have been undertaken on frontal sinuses by Forensic experts, Anatomist, ENT specialist and Surgeons. It has been found that no two frontal sinuses are alike4. This is important in differentiating the individuals and can be one of the important measures in establishing sex difference in frontal sinus of an individual. Considering the above facts the present study has been undertaken to study the frontal sinus with the help of ‘t’ test to establish the sexual dimorphism of frontal sinus.
MATERIAL METHODS Present study of frontal sinus was carried out in 80 randomly selected individuals. Roentrograms of their sinuses were taken and studied as follow. The normal radiographs of known age and sex available in department of radiology were studied. All the individuals were free from infection and fully developed frontal sinus. There ages were ranging from 18 to 40 years. The X-Rays taken by Water’s view selected. In this X-Rays 100 cm distance was kept constant between X-Ray tube and object. The X-Ray were marked ‘ L’ for males and F for females. Out of 80 X-Rays 51 were males numbered as L1 to L51 and 29 were female numbered as F1 to F29. Tracing of X-Rays To study the details of frontal sinuses the X-Rays were traced by keeping the X-Ray and tracing paper put on view box and traced out with minute details .This has facilitated the study of cells, configuration, septa, shape, height, breadth and area of measurement of sinus. Now this trace paper is placed on graph paper and again traced on graph paper. This gives X-Ray on graph paper.
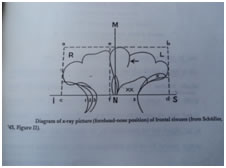
Figure 1 Figure 2: Measurement of height and breadth of Figure 3: Planimeter frontal sinus by schuller’s method6 Method of Measurement To study the frontal sinus in height, breadth and surface area following methods are used.
In order to calculate diameter, height, breadth, there is simple method.
Table 1
Measurement of Surface area by Planimetric Method7 I n this method an instrument called Planimeter is used from Civil Engineering department. It is basically used to measure surface area on large scale by post graduate students. Method of Measurement
RESULT AND OBSERVATION The study was done on both the sinuses that is left and right separately and combined in either sexes. Therefore in present study the age changes could not be studied. The results obtained were studied by applying the various statistical tests. Out of 80 X-Rays congenital absence of frontal sinus either unilateral or bilateral was not observed in single subjects. Schuller’s Method: Table 2: Height of Right, Left and Combined Frontal Sinus in Male and Female
The value of t’ test8 for height of Right, Left and Combined frontal sinus in either sex is 2.8,6.19 and3.49 respectively which is more than probability 0.05 according to ‘t’ table. So the values are highly significant. On the basis of Demarcating Point, the values of Average Height of Right, Left and Combined frontal sinus for males are >93,>49.6 and>70 respectively and for females are <0.2,<10.4 and<5 respectively. On the basis of % beyond DP, the values of Average Height of Right, Left and Combined frontal sinus for males are 0%,8.92% and12.5% respectively and for females are 0%,0% and57.59% respectively. From the above it is concluded that the Height of
Table 3: Breadth of Right, Left and Combined Frontal Sinus in Male and Female
The value of ‘t’ test for Breadth of Right, Left and Combined frontal sinus in either sex is 2.84,3.28 and3 respectively which is more than probability 0.05 according to ‘t’ table. So the values are highly significant. On the basis of Demarcating Point, the values of Average Breadth of Right, Left and Combined frontal sinus for males are >46,>52 and>49 respectively and for females are <4,<5 and<4.5 respectively. On the basis of % beyond DP, the values of Average Breadth of Right, Left and Combined frontal sinus for males are 8.92%, 3.57% and6.25% respectively and for females are 0%, 0% and0% respectively. From the above it is concluded that the Breadth of
With the help of Shullers method surface area can’t be measured, hence another Planimetric method is used for the accurate measurement of surface area, Height and Breadth. Table 4: Surface Area of Right, Left and Combined Frontal Sinus in Male and Female
The value of ‘t’ test for Surface area of Right, Left and Combined frontal sinus in either sex is 4.42,3.44 and4.10 respectively which is more than probability 0.05 according to ‘t’ table. So the values are highly significant. Above table shows the mean value for Right, Left and Combined frontal sinus for Male is 80,82 and82.8 respectively. While in Female is 43.3,49 and 45.7.On the basis of Demarcating Point 12.5% of Male and 30.76% of Females, the values of Average Surface area of Right, Left and Combined frontal sinus for males are >124,>139 and>131.5 respectively and for females are <34,<50 and<42 respectively. On the basis of % beyond DP, the values of Average Surface area of Right, Left and Combined frontal sinus for males are 12.5%, 8.92% and10.71% respectively and for females are 30.76%, 61.53% and 46.15% respectively. From the above it is concluded that the Surface area of
DISCUSSION The radiograph can play a great role in identification of individuals. The earlier workers had reported that no 2 sinuses were alike, Grey also reports the same thing. In present study the congenital abscency of any case was not reported in any X-Ray. Previously the same research was done by Dr.Uppe, there were 4 cases of congenital absency of frontal sinus. A study of frontal sinus can be performed at remote places where the finger print experts are not available. This study is easy and reliable. Radiographic study can also be performed in selected group of person’s foe example criminals for identification. Various workers like Culberd and Law in (1927), Thomas Poole in (1931), Mayer in (1935), Schuller in (1943),Uppe in (1984),Sahoo Gupta in (1993) were concluded the importance of frontal sinus. Dr.Uppe in his work stated that both the frontal sinuses were bigger in males than in females. The same conclusion is drawn by Schuller in (1943).He also stated that the size of left sinus is significantly bigger in both sexes as compared to right. The same observation is seen in present study. Likewise the maxillary sinus was also studied extensively for sexual dimorphism and personal identification. Percentage of agenesis is 6.2% in present study where as it is 5.28% in study done by Dr.Uppe and percentage of agenesis is only 1 % by schullers method. The present study is compared with the study done by Dr.Uppe in (1984). Table 5:
The above study shows that the findings of Dr.Uppe’s study correlate with present study. The slight variations in values are because of racial and geographic differences. The value of determining the sex by radiography is of medico legal importance and requires maximum accuracy.
CONCLUSIONS Frontal sinuses are bigger in males than in females. The left sinus is bigger in significant number of cases. Presence of septa and their number are always variable. Thus they also help in identification of an individual. The no. of arches is variable but their pattern is peculiar in every individual and thus they are helpful in identification of an individual. Supra orbital cells are commonly present in sinus. Their peculiar size, shape and position are variable, so it also helps in identification of an individual. Unilateral absence of sinus was seen 6.28% in present study where as the cases of agenesis was found to be 0% i.e. Not a single case with bilateral agenesis is found. Measurement of height, breadth and surface area are important three criteria in identification of an individual. But if one sinus absents then it can affect utility of method. At this time surface area is measured and used as important criteria for measurement. ‘t’ test is applied and sex is determined with the available resources, all the parameters of ‘t’ test are highly significant. Surface area measurement is done by Planimetric method .This method is an accurate method for calculation of surface area of frontal sinus. The area method of frontal sinus is a new concept for recording height and breadth. It may open a new vista in cephalometeric studies in coming generation.
REFERENCES
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Home
Home