|
Table of Content Volume 10 Issue 1 - April 2019
Morphological study of various shapes of coronoid process of known sex in dry human mandible in Saurashtra region
Balkrishna Thummar1, Jignesh Vadgama2*, Mital Patel3, Dilip Gohil4
1,2Assistant Professor, 3Professor, Associate Professor, Department of Anatomy, M P Shah Government Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat, INDIA. Email: dr_jigs_d@yahoo.co.in
Abstract The mandible, the largest and strongest bone of the face, serves for the reception of the lower teeth. It consists of a curved, horizontal portion, the body, and two perpendicular portions, the rami, which unite with the ends of the body nearly at right angles1.The coronoid process of the mandible is anterior projection process gives attachment of muscles of mastication. This study was done to identify various shapes of coronoid process of dry human mandible in Saurashtra region in reference to gender without considering age. The material for this study comprised of 131 (262 sides) dry human mandibles out of which 79 are male (158 sides) and 52 are female (104 sides) from the osteology bank of Anatomy Department, M P Shah Govt. Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat, India. We observe three different variants of coronoid process namely triangular, rounded and hook shaped. We got 64.56% and 32.69% of triangular shaped, 12.66% and 28.85% of hook shaped and 22.78% and 38.46% of rounded shaped in male and female mandibles respectively. This study of shape of coronoid process will be beneficial for the Anthropologists, Forensic scientists and Reconstructive surgeons Key Word:Mandible, Coronoid process, Triangular, Rounded, Hook
INTRODUCTION The mandible, the largest and strongest bone of the face, serves for the reception of the lower teeth. It consists of a curved, horizontal portion, the body, and two perpendicular portions, the rami, which unite with the ends of the body nearly at right angles1. The rami bear the coronoid and condylar processes. The coronoid process projects upwards and slightly forwards as a triangular plate of bone. Its posterior border bounds the mandibular notch, and its anterior border continuous into that of the ramus. The coronoid process is derived from a Greek word “korone” meaning “crow’s beak”2.The mandible or the submaxilla is a U shaped bone having curve shaped body with 2 rami. Each rami has coronoid and condylar processes. The coronoid process develops as a discrete entity within the mass of temporalis muscle. This process gives attachment to important muscle of mastication – Temporalis muscle attached to apex whole of the medial surface and anterior border and enchroching partially on its lateral surface. Rest of the lateral surface gives attachment to masseter3. Clinically, it is important as it is a membranous bone which can be removed intraorally without any functional deficiency and facial disfigurement for reconstruction of orbital floor deformities, alveolar defects, paranasal sinus augmentation, non-union fractures of mandible, osseous defect reconstruction, and other repairing procedures in craniomaxillofacial surgeries4. There exist variations in the shape of the coronoid process. The shape of the coronoid process is considered to be very useful in the field of anthropology and forensic science as it acts as an evolutionary marker5. The aim of this study is to note the incidence of the shapes of coronoid process in male and female mandibles.
MATERIAL AND METHOD The present study was carried out in the Department of Anatomy, M P Shah Govt. Medical College, Jamnagar. A total of 131 dry adult human mandibles were included in the study which consisted of 79 male and 52 female mandibles. The mandibles with damaged coronoid process were excluded from the study. The coronoid process of both the sides were included, a total of 262 sides. Variations in the shapes of the coronoid process were noted down. Three different variants of the shapes were observed and were classified into triangular, hook, rounded shaped. The shapes were studied bilaterally and in both the genders. The gender of the mandible was determined using non- metric analysis. The heaviness, muscular markings, chin shape and gonial eversion were considered in the determination of gender.
OBSERVASIONS AND RESULTS Three types of coronoid process were observed.
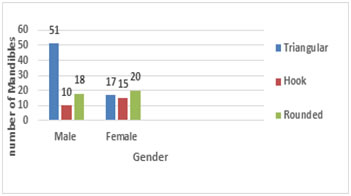
Triangular shape was observed in 102 (64.56%) sides in male and 34 (32.69%) sides in female as per figure 1. Hook shape was observed in 20 (12.66%) sides in male and 30 (28.85%) sides in female as per figure 2. Rounded shape was observed in 36 (22.78%) sides in male and 40 (38.46%) sides in female as per figure 3.
Figure 1: Triangular coronoid process Figure 2: Hook shape coronoid process Figure 3: Rounded coronoid process Table 1:Gender difference observed in the shape of coronoid process
Figure 4: Bar diagram showing gender wise distribution of various shapes of coronoid process
Table 2: Comparison of various studies on the shapes of coronoid process in relation to gender with other studies
DISCUSSION As per Table 2 we compare our study with Issac (2001)6; Akram Hossain et al(2011)7; Vipul et al(2014)8 and Pradhan et al.(2014)9. In all above study except Akram Hossain et al(2011)7, most common shape of coronoid process in male and in female is triangular and least common is hook shaped. In Akram Hossain et al(2011)7most common in male and female is hook shaped. In our study we reported triangular shape as most common in male which is correlated with the most of the studies mentioned here except Akram Hossain et al(2011)7.In our study we reported hook shaped as least common in male which is correlated with Vipul et at(2014)8 and Pradhan et al.(2014)9. In our study we reported round shaped as most common in female which do not correlate with the above compared studies. In our study we reported hook shape as least common in female which is correlated with Vipul et at(2014)8 and Pradhan et al.(2014)9.
CONCLUSION In the present study most common shape in male is triangular followed by rounded and least common is hook shaped. While in female most common is rounded followed by triangular and least common is hook shaped. So hook shaped coronoid process is least common in both male and female. Detailed knowledge of variant morphological shapes of coronoid process is important got anatomist, anthropologist and forensic researchers. It is also helpful for reconstructive surgeons as it is used as graft and as donor site for sinus augmentation.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT We thank the Department of Anaotmy, M P Shah Govt. medical college, Jamnagar for permitting us to study.
REFERENCES
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Home
Home