|
Table of Content Volume 7 Issue 2 - August 2018
The morphometric study of the jugular foramen in human adult skulls of Western Maharashtra
Avinash D Shewale1, Swati Lalasaheb Patil2*, Rohini Rajesh Karambelkar3
1Associate Professor, Department of Anatomy, Yogita Dental College, Khed, Chiplun, Maharashtra, INDIA. 2Assistant Professor, 3Professor and HOD, Department of Anatomy, Prakash Institute of Medical Sciences and Research, Islampur, Sangali ,Maharashtra, INDIA. Email: drswatipatil1612@gmail.com
Abstract Aims and objectives: To study and compare the anthropometric measurements of jugular foramina in human adult skulls of Western Maharashtra. Material and methods: This study was carried out on 100 dry skulls with 65 male and 35 female skulls in the Department of Anatomy, Prakash Institute of Medical Sciences and Research, Islampur. Digital vernier caliper was used to take the jugular foramen measurements of both sides. Parameters were length and width of jugular foramen. The data was analysed by using SPSS version 16.0. Observation and results: All the parameters were significantly larger on right side than left one in both males and females which was statistically significant. Conclusion: The measurements of bilateral jugular foramen of males and females obtained in the study may be helpful for neurosurgeons, radiologists and forensic experts as it contain significant vessels and neural structure Key Word: morphometry, jugular foramen, neurosurgeon
INTRODUCTION The jugular foramen is a depression located at the posterior end of the petro-occipital suture. It is formed by the petrous temporal bone anterolaterally and the occipital bone posteromedially. It courses anteriorly then laterally and finally inferiorly through skull base1. It consists of a smaller anteromedial portion (pars nervosa) and a larger posterolateral portion (pars vascularis) that are separated by a complete or incomplete fibrous or bony septum. The pars nervosa contains the glossopharyngeal nerve and inferior petrosal sinus. The pars vascularis contains the internal jugular vein, the vagus nerve and spinal part of accessory nerve. Within the jugular foramen glossopharyngeal nerve gives off the tympanic branch called the nerve of Jacobson and the auricular branch of vagus nerve i.e. Arnold’s nerve2. The jugular foramen is separated from the hypotympanum by a bony plate and is medial to the descending facial canal. It is separated from the anteromedial carotid canal by the caroticojugular spine and from the inferomedial hypoglossal canal by the jugular tubercle. The sigmoid sinus courses anteriorly into the jugular bulb3. The jugular foramen varies in size and shape in different crania, from side to side in the same cranium, from its intracranial to extracranial end in the same foramen because of its complex irregular shape, its curved course and its formation by two bones. It is generally said that the size, height and volume of jugular foramen vary in different racial groups and sexes4,5. It is important to know the morphology of the jugular foramen because intracranial and extracranial lesions may affect the jugular foramen in addition to intrinsic abnormalities.
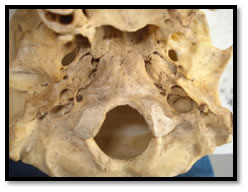
MATERIALS AND METHODS Total 200 jugular foramina were examined from 100 adult dry skulls with known male and female differentiation. The skulls were obtained from the department of Anatomy, Prakash Institute of Medical Sciences and Research, Islampur. The length, width, and presence or absence of bony septum was observed. The measurements were taken by using sliding digital vernier caliper. A comparison was made by means of the dimensions using paired t test. The mean, standard deviation and range of each dimension was calculated. Right and left side differences in male and female skulls were analysed. Figure 1: Arrow showing jugular foramen in dry skull OBSERVATIONS AND RESULTS: Table No 1: Comparison of male right vs female right jugular foramen
Table No 2: Comparison of male left vs female left jugular foramen
Table no 3: Comparison of male right vs left jugular foramen
Table 4: Comparison of female right vs left jugular foramen
RESULTS
The tables showed the measurements and comparison of results of jugular foramina in the skulls included in the study, according to genders were tabulated. The data showed in table no 1 and 2, predicted that no significant differences in jugular foramina length and its width of male and female right and left sides. The dimensions of the jugular foramina of males and females depicted higher values in males as compared to females except the length of the jugular foramen on left side. The table no 3 and 4 showed comparison of male right and left ear, female right and left ear respectively, which showed right sided jugular foramina had significantly higher values as compared to left one.
DISCUSSION The size and shape of the jugular foramen is much variable and is related to the size of internal jugular vein. The right jugular foramen is usually larger than the left but because of wide variations in the anatomy of structures passing through it accounts for the variation in size and shape of jugular foramen. The size of internal jugular vein is variable in right and left sides. It is already visible in the human embryo at the 23mm stage and probably results from differences in the pattern of development of right and left brachiocephalic veins6. Rhoton et al (1975) studied the morphology of jugular foramen and they noted that 68% of jugular foramen was larger on right, 12% equal, 20% smaller7. In Sturrock’s investigation of 156 skulls, the right foramen was larger in 68.6%, the left larger in 23.1% and equal on both sides in 8.3%6. Hatiboglue and Anil studied 300 Antolian skulls from the 17th and 18th centuries and observed that in 61.6% the jugular foramen was larger on the right side and in 26% it was larger on the left side and in remainder of equal size8. Patel and Singel studied 91 Indian skulls and observed in 60.4% cases larger right foramen, in 15.4% larger left foramen and in 24.2% equal on both sides9. Hussain Saheb S et al (2010) studied the 250 jugular foramina and in 55% cases right jugular foramen was larger while in 25% left jugular foramen was larger. In 20% cases it was equal on both sides6. In our study we observed larger right jugular foramen in 80%, left foramen in 20% and it is equal in 1.5% cases in males. While in females right jugular foramen larger in 71%, left larger in 28.57%, and equal in 0.42% cases. Hovelacque was the first to propose the subdivision of jugular foramen. The foramen is divided by a fibrous or bony septum that joins the jugular spine of the petrous bone to the jugular process of the occipital bone into an anteromedial and a posteromedial compartment6. Tekdemir et al observed no partition in their studies while Ekinci et al found bony bridges in 20% and tripartite jugular foramen in 0.7%6. In Sturrock’s investigation, he observed complete separation on right side in 3.2%, on left side in 3.2% and partial separation on right side in 1.3% and partial separation on right side in 1.3% and on left side it was 10.9%10.
CONCLUSION The jugular foramen contains significant vessels and neural structures. The present study observed that right jugular foramen is larger than the left one when studied on 100 dry skulls. Same was observed in previous studies done by various authors. These findings will be useful for neurosurgeons, radiologists and forensic experts.
REFERENCES
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Home
Home