Official Journals By StatPerson Publication
|
Table of Content Volume 6 Issue 3 - June 2018
The efficacy and adverse effect profile of lithium versus Divalproex sodium in the treatment of patients with bipolar affective disorders on combination therapy - A comparative, naturalistic, clinical study
Rovin C Vincent1, Vijayalaxmi MK2*, Nicole Pereira3
1ExPG, 2Associate Professor, 3Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmacology, Father Muller Medical College, Mangalore 575002, Karnataka, INDIA. Email: rovinvims@gmail.com
Abstract Objective: To compare the efficacy of Lithium versus Divalproex sodium in the treatment of patients with bipolar affective disorder on combination therapy. Methods: A prospective, comparative study was done comparing the efficacy of Lithium versus Divalproex sodium in the Treatment of Bipolar Disorder. Patients aged between 18 to 65 years of age of either sex diagnosed with Bipolar Disorder were included in the study. Efficacy was analysed using the YMRS scale at Baseline and at the end of 4 weeks. Results: A total 68 Bipolar Disorder patients with current episode mania, were incorporated in the study. They were divided into 2 groups. One group was on Divalproex sodium and the other group on Lithium. The concurrently administered drugs were comparable between both the groups. A total of 50 patients were males and 18 patients were females. YMRS scoring was done at baseline and at the end of 4weeks. In the Divalproate sodium group the YMRS scores at baseline and at 4 weeks were 31.22 and 29.13 respectively. In the Lithium group the YMRS scores at baseline at and 4 weeks were 30.88 and 28.93 respectively. In both the groups there was a significant reduction in the YMRS scores in 4weeks with a p value of less than 0.05. However when the YMRS scores were compared between the two groups at the end of 4 weeks there was no statistical difference. The efficacy was same in both the groups. Conclusion: Both Lithium and Divalproate Sodium were equally efficacious in the treatment of Bipolar disorder at the end of 4 weeks of treatment. Patients showed significant improvement with both the drugs at the end of 4 weeks. Key Words: lithium, divalproex sodium.
INTRODUCTION Bipolar disorder is a complex psychiatric disorder with significant individual and social implications. It requires complex pharmacological treatment.1 Bipolar disorder is characterized by fluctuations in mood, from elation to depression. This disorder can cause major disruptions in family and social life. A study from the UK suggests that for patients with bipolar disorder, one year after hospital discharge, mortality was higher than that of the general population.2 The prevalence of Bipolar Disorder is increasing over the past few years3 and this calls for studies in this area. Currently the first line drugs used in the treatment of bipolar disorders are lithium and divalproex sodium. However in clinical practice one second generation atypical antipsychotic drug is often added to control the agitation, over activity and psychotic symptoms. Lithium was the first agent shown to be useful in the treatment of bipolar disorder. It has been used for more than 60 years. It continues to be used as the major mood stabilizing agent both in acute phase illness and in maintenance treatment. However due to the slow onset of action and frequent need of therapeutic drug monitoring other drugs are being used. One such drug is the antiepileptic drug divalproex sodium. This study in undertaken to compare the efficacy of Lithium versus Divalproex sodium in the treatment of patients with bipolar affective disorder on combination therapy.
MATERIAL AND MEHODS This was a prospective, Comparative Hospital based study. It was conducted between May 2013 and May 2014 in Department of Psychiatry, Father Muller Medical College. The sample size was 68. Ethical Clearance was taken from the Institutional Ethical Committee. An informed written consent was taken from every patient included in the study. Patients aged between 18 years and 65 years of either sex diagnosed to have Bipolar Affective Disorder with current episode mania or hypomania admitted in the in-patient ward were included in the study. Patients with significant co-morbid medical or psychiatric conditions were excluded from the study. 36 Bipolar Disorder patients on Divalproex sodium were included in one group and 32 Bipolar disorder patients on Lithium were included in the other group. A brief history and examination were carried out in each patient. The data was entered in a proforma sheet. The investigations carried out were noted. YMRS scoring was done at baseline. The patients were followed up for a period of 4 weeks. The YMRS scoring was done again at the end of 4 weeks. Adverse drug events, if any were recorded. The collected data was analysed using Mean, Frequency, Percentage, Standard Deviation, paired and unpaired t test, chi-square test. RESULTS Figure 1 shows the age distribution of the sample size. Figure 2 shows the distribution of sample size according to gender. Males contribute the predominant gender in the study. Table 1 shows the age of first onset of Bipolar disorder. Patients were maximum in the age group of 31-40. Table 2 shows the distribution of the study sample based on Polarity of the first episode. The first episode diagnosed was predominantly mania. Table 3 shows the total duration of the illness. Table 4 show the YMRS scores between the groups and Table 5 shows the paired sample test. YMRS scoring was done at Baseline and at the end of 4weeks. In the Divalproate sodium group the YMRS scores at baseline at 4 weeks were 31.22 and 29.13 respectively. In the Lithium group the YMRS scores at baseline at 4 weeks were 30.88 and 28.93 respectively. Both the groups had a significant reduction in the YMRS scores in 4weeks with a p value of less than 0.05. However when the YMRS scores were compared between the two groups at the end of 4 weeks there was no statistical difference. The efficacy was same in both the groups.
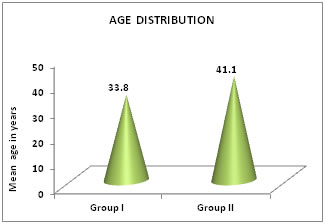
Figure 1: Graph showing the age distribution
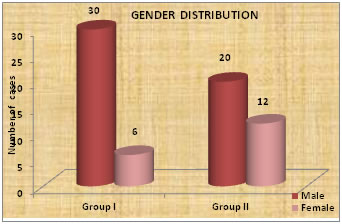
Figure 2: Graph showing the distribution of the study sample according to gender
Table 1: Table showing the age of first onset of Bipolar Disorder
p value Table 2: Table showing the distribution of the study sample based on Polarity of the first episode
p value 0.626
Table 3: Table showing the total duration of the illness
p Value 0.150
Table 4: Table showing the YMRS scores between the two groups
Table 5: Table showing the Paired Samples Test
DISCUSSION The treatment of bipolar depression is a major challenge. Treatment can be successful if the correct diagnosis is made and there is early initiation of treatment. The present study evaluated and compared the efficacy of Lithium versus Divalproex Sodium in the treatment of Bipolar Disorder. A total of 68 patients were included in the study who were divided into 2 groups. In the Divalproex Sodium group 36 patients were included of which 4 were lost to follow up. In the lithium 32 patients were included of which 2 were lost to follow up. A total of 62 patients were thus available for evaluation. The mean age group of the patients in this study was 33.8 years in the Divalproate Sodium group and 41.1 years in the Lithium group. A similar study was done by Kessing LV et al which compared the efficacy of Lithium and Divalproate Sodium in the treatment of Bipolar Disorder. In that study the mean age of the patients belonging to the Divalproate group was 52 years and the mean age of the patients belonging to the Lithium group was 49 years. (1) In the present study a total of 73.5% patients were males and 26.5% patients were females. The study done by Kessing LV et al had 58% females and 42% males. (1) However most studies report a nearly equal male-to-female ratio in the prevalence of bipolar disorder.4 In this study the onset of the disorder is more in the age group of 18-30years with 33.8% of the study population belonging to this group. This is followed by the age group of 31-40 years with 23.5% of the study population belonging to this age group. The least number of patients were in the age group of 51-64 years with 5.9% of the population belonging to this age group. The study done by Kessing LV et al show that the mean age of onset of the disorder is about 21 years.1 Most of the patients had mania as the first episode of the Bipolar Disorder. A total of 65 out of 68 patients had mania as the first episode of the Bipolar Disorder. Sadock BJ reported that in Bipolar Disorder, the first presenting symptom is mania.5 In this study most of the patients had a total duration of the illness ranging between 5 to 10 years with a total of 30.9% of the study population belonging to this time duration. The total duration of the illness was comparable between the two groups with a p value of 0.150. This study concluded that there was a significant statistical difference in the YMRS scores after 4 weeks of treatment in both the Lithium and divalproate groups. However the efficacy of both the groups were comparable with no statistical significance. Thus both the drugs were equally efficacious at the end of 4 weeks. Bowden CL et al carried out a randomized, double-blind, parallel-group study to compare the effectiveness of divalproex sodium with that of lithium and placebo in patients with acute mania. The study concluded that both divalproex sodium and lithium were significantly more effective than placebo in reducing the symptoms of acute mania.6 Freeman TW et al (7) carried out a study to compare the efficacy of lithium carbonate with that of valproate in acute mania. The study concluded that lithium and valproate were both effective in improving manic symptoms, and lithium was slightly more efficacious overall. BALANCE trial which compared lithium monotherapy with valproate monotherapy in treatment of Bipolar Disorder showed a decreased need for intervention initiation for an emergent mood episode.8 A population-based, nationwide register linkage study was done by Kessing LV et with a follow up period of 12 years. A total of 4268 participants were included among whom 719 received valproate and 3549 received lithium subsequent to the diagnosis of bipolar disorder. The rate of switch/add on to the opposite drug (lithium or valproate), antidepressants, antipsychotics or anticonvulsants (other than valproate) was increased for valproate compared with lithium. The rate of psychiatric hospital admissions was increased for valproate v. lithium.The study concluded that treatment with lithium was in general and overall superior to treatment with valproate.1 It is seen that lithium is effective in patients with typical Mania and Divalproate Sodium is more effective in patients with co morbid conditions. (5) The present study confirmed this as Divalproate Sodium was preferred to be given in Bipolar disorder with co morbid conditions.
CONCLUSION The treatment of Bipolar Disorder is a challenge. Early diagnosis and treatment is the key for the successful management of patients with Bipolar Disorder. The present study concluded that both Lithium and Divalproate Sodium were equally efficacious in the treatment of patients with Bipolar disorder with current episode mania, at the end of 4 weeks of treatment. Patients showed significant improvement with both the drugs at the end of 4 weeks. Both the drugs were well tolerated. However bigger studies involving a larger sample size and carried out for a longer duration of follow up is required to reemphasize this study.
REFERENCES
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Home
Home