Official Journals By StatPerson Publication
|
Table of Content - Volume 11 Issue2 - August 2019
Study of stress amongst parents of health professionals: A comparative cross-sectional study
Nitin Joshi1, Ruth Joshi2*
1,2Professor, Department of Physiology, Smt. Kashibai Navale Medical College and General Hospital, Narhe, Pune, Maharashtra, INDIA. Email: ruthnjoshi@yahoo.com
Abstract Background: The process of becoming a doctor and achieving a doctors degree is of long duration process where we need to go through 5 to 6 hectic academic years. Workplace related stress is estimated to be the biggest occupational health problem all over the world after musculoskeletal disorder such as back problems and stress related sickness. Doctors are no doubt the prime care givers who undergo tremendous stress. The syllabus loads, personal problems, emotional problems, lack of assertiveness, lack of self-confidence are some of the sources of stress to health course students. The level or degree of stress caused by these sources has to be assessed. Aims and objectives: To assess the stress experienced and coping strategies adopted by the parents of children. Material and Methods The study was conducted in the Department of Physiology Smt. Kashibai Navale Medical College & General Hospital, Narhe, Pune. The study included 50 Parents of students admitted to one of the health professional course of the age group of 35 to 55 years out of which 25 were parents of normal students and 25 were parents of students diagnosed with some psychiatric problem. Results: Parental distress was 30.64 ±0.81, difficult child characteristics were 24.32±1.18, dysfunctional parent child interaction was 11.76 ±1.26 and total stress score in cases under study was 68.07 ±27.16. Conclusion: Over the recent years there has been growing concern about stress in health professional course. But a little is done to manage the stress shared by family members. Hence a health educational approach to impart knowledge about managing stress has to be delivered. Key Word: stress.
INTRODUCTION Stress is defined as the non specific response of the body to any demand made on it (Seyle, 1976). Education related stress is now a subject of concern to parents and society as well. It results in poor performance and also personal life becomes increasingly unhappy1. Doctor is a noble profession and a profession practiced all over the world but is subjected to a huge degree of stress. The process of becoming a doctor and achieving a doctors degree is of long duration process where we need to go through 5 to 6 hectic academic years. The labour force survey 2004-05 estimated that every year two million people are suffering from stress, which they believed was caused or made worse by their current or past work2. The World Health Organization called job/education stress a “World wide endemic” and the 1993 UN report called job/education stress the “20th Century epidemic”. Workplace related stress is estimated to be the biggest occupational health problem all over the world after musculoskeletal disorder such as back problems and stress related sickness. Stress leads to lack of continuity in study and concentration. It also creates health issues and have higher sickness rates. Some of the serious complications may extend to psychological disturbances. It has been suggested that stress may be a reason for leaving their professional course midway. Doctors are no doubt the prime care givers who undergo tremendous stress. The syllabus loads, personal problems, emotional problems, lack of assertiveness, lack of self confidence are some of the sources of stress to health course students. The level or degree of stress caused by these sources has to be assessed. The present study was undertaken to find out the stress experienced and coping strategies adopted by the parents of children
MATERIAL AND METHOD Approval of institutional ethics committee was taken prior to commencement of this study. The study was conducted in the Department of Physiology in our college. The study included 50 Parents of students admitted to one of the health professional course of the age group of 35 to 55 years out of which 25 were parents of normal students and 25 were parents of students diagnosed with some psychiatric problem. The information of participants for the study was collected from administration office of college for subject group and control group. Data was collected and analysed through the parenting scale index developed by Abidin. The Parenting Scale Index, Short Form- Abidin3 The Parenting Scale Index, Short Form- Abidin3: It was developed to identify parent- child dyads under stress and consequently at risk for dysfunctional parenting and development of emotional pathology in children. The Parenting Stress index was standardized for use with parents of children from 1 month to 12 years of age. The scale has 36 items and the items are scored on 5 point scale 1) SA (Strongly Agree), 2) A (Agree), 3) NS (Not Sure), 4) D (Disagree), and 5) SD (Strongly Disagree). It has three major dimensions. The dimensions are Parental distress, difficult child characteristics, Parent- child dysfunctional interaction. The scores indicate that higher the score, higher the stress and vice versa The questionnaires were given to the participants and responses were collected Exclusion Criteria:
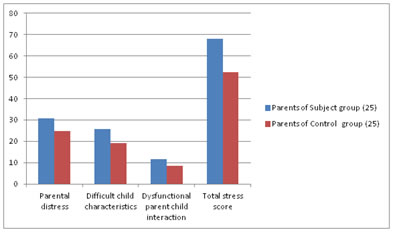
OBSERVATION AND RESULT Data was analysed by SPSS, Version 14 software. A total of 50 Participants (25 Parents of Subject group and 25 Parents of Control group) were included in the study. The mean age (in years) was 36.96 ± 1.27 and 36.84 ± 1.21 in subject and control group respectively. There was no significant difference in the age in the two groups (p = 0.7338). (Table1, Graph1) Table 1: Comparison of stress level
Graph 1: Comparison Of Stress level DISCUSSION The present world is a fast changing world. There are lot of pressures and demands on students for which they face various types of stress. Doctors profession has become a most preferred profession amongst students nowadays, of which stress is a inseparable part and a doctor cannot get away from it. Hence the present study was designed to assess the level of stress amongst students of health professional course. The stress level adopted by parents were assessed by The Parental Stress Index in which the respondents were assessed on three major stress domains such as (1) Parental distress (2) Dysfunctional parent- child interaction (3) Difficult child characteristics. Comparison of parental stress between group I and group II Respondent in Group I exhibited more stress than Group II (Table 1) in all the domains and in total score as well. It is very obvious that parents of subject group experience higher level of stress when compared to parents of control group. It can be related to various factors such as the expectation not met, difficulties in dealing with a child, poor family resources as many are from a nuclear family background, stigma, societal attitude and so on. The similar results were found in the studies by Vidyasagar and Koshy25 and, who found that the parents of subject group experienced more stress then parents of normal children. The similar study was also conducted by Campbell51, who found that parents of subject group reported higher stress levels than parents of control group. The stresses of parenting include prolonged dependency and demands for special care and worry regarding future self-sufficiency. Isolation from family and friends, and the unpredictable, ambiguous nature are important sources of life stress that impose physical and emotional strains on parents exceeding levels experienced by parents of normal children52.
CONCLUSION The following conclusions were drawn based on the findings of the present study. Over the recent years there has been growing concern about stress in health professional course. Various studies have shown that stress not only affects the individual but also their family. But a little is done to manage the stress shared by family members. Hence a health educational approach to impart knowledge about managing stress has to be delivered.
REFERENCES
|
|
 Home
Home