Official Journals By StatPerson Publication
|
Table of Content - Volume 7 Issue 1 - July 2018
A study on the preferences of first year MBBS students about different teaching and learning methods
Sanghamitra Panda1*, Abdul Raoof Omer Siddiqui2, Nikhat Yasmeen3, Aiesha Durrebar Younus Khan3, Ratna Kumari N3
1Professor, 2Associate Professor, 3Assistant Professor, Department of Physiology, Shadan Institute of Medical Sciences, Peerancheruvu, Hyderabad, 500008, Telangana, INDIA. Email: dr.sm.panda@gmail.com
Abstract Background: There is a paradigm shift in medical education in recent years as it has become increasingly student centric from a traditional teacher centric practice. Opinions and preferences of Students are paramount before the introduction of any new methods or modifications in existing methods of teaching. This present study was conducted on 1st year MBBS students to know their preferences about different teaching and learning methods practiced by teachers. Materials and Methods: The study group included 138 first year MBBS students among them 81 were girls and 57 were boys. A pre-designed questionnaire was administered to all the participants regarding their opinion and preferences about various teaching and learning methods like lecture based learning (LBL), tutorial, group discussion (GD), seminar, problem based learning (PBL) and Jigsaw practiced by Physiology faculty members during teaching sessions. Results: Students preferred PBL over other teaching methods for better analysis (47%). Among all teaching tools they liked PBL the most and wanted more PBL classes (31%) to be conducted. 28% students stated LBL classes are needed for better understanding. 49% students opined that they are motivated to read the topic after tutorial classes. 27 % students expressed seminars improved their confidence level where as 40% told they get better concept by group discussions. Conclusion: PBL was the most liked method by the Students in many aspects in comparison to other teaching learning methods. Though PBL was preferred the most but other teaching methods too were chosen by students for better understanding, improving their concept and confidence. Each method of learning has its own merits and demerits. Therefore different teaching learning tools should be adopted in medical schools instead of only one or two, so that students will be benefitted in all aspects of learning. Key Word: PBL, teaching methods, LBL, group discussions.
Medical education recently witnessed an exemplar shift. Majority of medical schools have adapted newer methods of teaching and learning with a shift from didactic teacher centered teaching to student-centered learning1. Opinions and preferences of students are paramount before the introduction of any new methods or modifications in the existing methods of teaching. Teaching excellence in medical curriculum can be strengthened by assessing students’ perception regarding different teaching techniques. Students’ involvement and active participation plays a great role to generate interest in the topic. Teaching techniques should stimulate critical thinking and better analytical problem solving ability2,3 in students. Didactic lecture is the oldest and most commonly adopted method to teach a large gathering of students. Although it has many merits, it is teacher centric and has very little opportunity for a student to interact and does not even initiate the method of problem solving and critical thinking. On the other hand PBL helps in self directed learning, lateral thinking and clinical reasoning4. Students have different approach to learn, they adopt different methods for learning. Each method of learning has its pros and cons. Methods like tutorial, seminar; group discussion and jigsaw too have many merits. In a tutorial class students can get individual attention from the teacher and it encourages learners to incorporate conceptual knowledge. It opens avenues to learn more. Some time the student might have skipped some important points and concept of a topic. During the tutorial classes all these lacunae can be covered which had been omitted during regular lecture classes.5 A properly organized seminar offers attendees a wealth of information in one place in a short period of time. Seminar often features several speakers, providing information on a particular topic. Students who attend seminars learn new ideas and skills which help them improve their concept and those who present seminars gain by development of their oral presentation skills, improves motivation and confidence in them.6 Group discussion plays a vital role in understanding the topic. Discussing the topic with teachers and friends helps in learning the topic with perfection. It involves sharing of learning, which equally benefits all the participants. It helps to know about the mistakes and weaknesses of a student. It polishes the study skills and exam preparation skills7,8 Jigsaw can be an efficient cooperative learning strategy where students are directly engaged with the material, instead of having material presented to them, which fosters depth of understanding. Students gain practice in self teaching, peer teaching, which requires them to understand the material at a deeper level. It encourages cooperation and active learning as well as gives value to the contribution of each student. 9 Problem based Learning (PBL) is a student-centered teaching learning tool that involves students actively working together to solve real-world problems. It encourages students to use higher order critical thinking and improves problem solving abilities. Learning is student-centered. The instructor acts as a facilitator.10,11 This present study was conducted in 1st year MBBS students to know their preferences regarding different teaching and learning methods practiced by teachers.
MATERIAL AND METHODS A cross sectional study was carried out during the period of February to May 2017 amongst first year undergraduate medical students attending physiology in a medical college. Out of 150 students, 138 were participated in the study. Among the participants 81 students were girls and 57 were boys. Informed consent was taken from all the students before commencement of the study. A pre-designed questionnaire was used as a tool to collect the data regarding their opinion and preferences about various teaching and learning methods such as; lecture based learning (LBL), tutorials, group discussion (GD), seminars, problem based learning (PBL) and Jigsaw which had been practiced by Physiology faculty members during teaching sessions. The questionnaire included questions pertaining to best rated teaching method and proposed reason for the preferred teaching method. The data was collected from students maintaining confidentiality. A briefing was given about the objective of the study to all the participants. Institutional ethical committee approval was obtained before the commencement of the study. All the data was entered in Microsoft Excel spreadsheets and was analyzed using percentages.
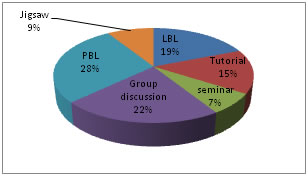
RESULT In the present study the mean age of the students was 19. 09 ± 0.48 years. Among all the teaching methods adopted PBL was the most liked method (28%), followed by group discussion (22%) and seminar was the least preferred method by the students. Table 1 depicts the preferences of students about different teaching and learning methods. Among the six criteria included in the study to assess their preferences, PBL was preferred by majority of students for better analysis and lateral thinking. 47% (65 out of 138) of the students preferred PBL over other methods as it helped them in better analysis of the topic and 32% of the students had the opinion that PBL helped them in lateral thinking and understanding the subject better than other teaching methods. 31% of students wanted more PBL sessions to be incorporated in the curriculum in comparison to other methods. The most preferred method chosen by the students for each parameter of learning is depicted in Table 2. 28% of students rated LBL as the most suitable teaching method for understanding the subject well. 49% of the students were of view that tutorials motivated them to study more about the topic covered. 40% of the students felt that group discussions helped them to understand the concept better than other teaching methods. 27% of the student said that seminars improved their confidence on the topics they presented. Majority (94%) of students agreed that small group teaching is the teaching method of their choice as it helped them to understand the topic better than in a large group. All the 138 students (100%) opined that group interactions are necessary to learn the topic well and they were of the view that teachers should adapt various teaching methods instead of adopting only one or two methods to make the subject more interesting, easy to understand and to have a better concept. Table 1: Preferences of students about different teaching and learning methods (n= 138)
Table 2: Most preferred method for each parameter of learning
Among the six methods practiced students liked PBL the most (28%) followed by group discussion (22%) and the Jigsaw method was least preferred (9%) which is portrayed in graph 1.
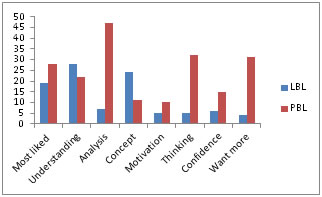
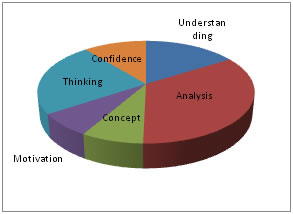
Figure 1: Student preference about most liked teaching method (n=138) Graph 2 shows the comparison of student’s preferences between LBL and PBL. Students liked PBL in comparison to LBL in analyzing the topic. It also motivated them to learn the topic more, helped them in lateral thinking, improved their confidence. They preferred LBL over PBL to understand the topic and get better concept. Figure 2: Comparison of student’s preferences between LBL and PBL Graph 3 depicts student’s preferences regarding PBL teaching technique. More students preferred PBL for better analysis and lateral thinking.
Figure 3: Student’s preferences regarding PBL
DISCUSSION In this study, among the six different teaching-learning methods adopted, majority of the students (47%) expressed that PBL leads to better analysis of the topic and stimulates lateral thinking. Findings of this study are supported by Salwani Ismail et al who observed that PBL method is preferred over other methods12,13. This may be due to the fact that PBL is an active learning process, discussion during these sessions helps students identify the learning issues necessary to understand the subject well and lead them to seek information through individual and self directed study. It encourages independent learning and deeper understanding of any particular topic. Several studies also found that PBL is the most effective teaching method as it enhances critical thinking and analysis. Group discussion was preferred by the students in learning the concepts well as group discussions are conducted in small groups and students get the opportunity to clarify their doubts, and hence it helps the students to learn the concept effortlessly. Interacting with other students during group discussion sessions enable them the opportunity to trade ideas and discuss issues with peers. Students favored LBL over other methods of teaching in understanding the subject. A similar study by Padmanav TS et al also observed that LBL is preferred by first year MBBS students to understand the topic. Didactic lectures provide background information of any particular topic which is explained in an elaborative manner so that it becomes easy for the students to understand [14, 15]. Students who are auditory learners may find it appealing to their learning style. Only demerits of didactic lecture is it tends to place the audience in a passive role, students may be busy taking notes and have very little time to reflect, question or analyse and synthesise ideas. 27% of students chose seminar as the better method to build up confidence, as in seminars students study the allotted topic extensively and present it in front of an audience which makes them more confident. Bruton PA et al also had similar findings in their study where students were of the opinion that seminar-based learning is more effective, more relevant to self development and more interactive than formal didactic lectures.16 49% of students expressed that they were more motivated to learn the topic with tutorial sessions than other methods; this may have been due to the fact that in tutorial sessions, students receive an individualized learning experience which they can’t always get in a classroom setting. Students get the freedom to ask questions, it improves their self esteem and confidence so they get motivation to study the prescribed topic and excel. The study findings in our study are similar to a study conducted by Kumar RP et al who observed that tutorial is an effective teaching learning tool for undergraduate medical students.17 Majority of students participated in the study stated that small group teaching and group interactions are a must to learn and understand the topic well.
CONCLUSION Student feedback is a useful method to know their preferences regarding different teaching techniques to make the curriculum more effective. From this study it is evident that students are more interested in student centric, more interactive learning methods like PBL, group discussion and tutorial over didactic lectures which is more teacher centric and involves only one way communication.
REFERENCES:
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Home
Home